Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking Stainless Steel Temperature
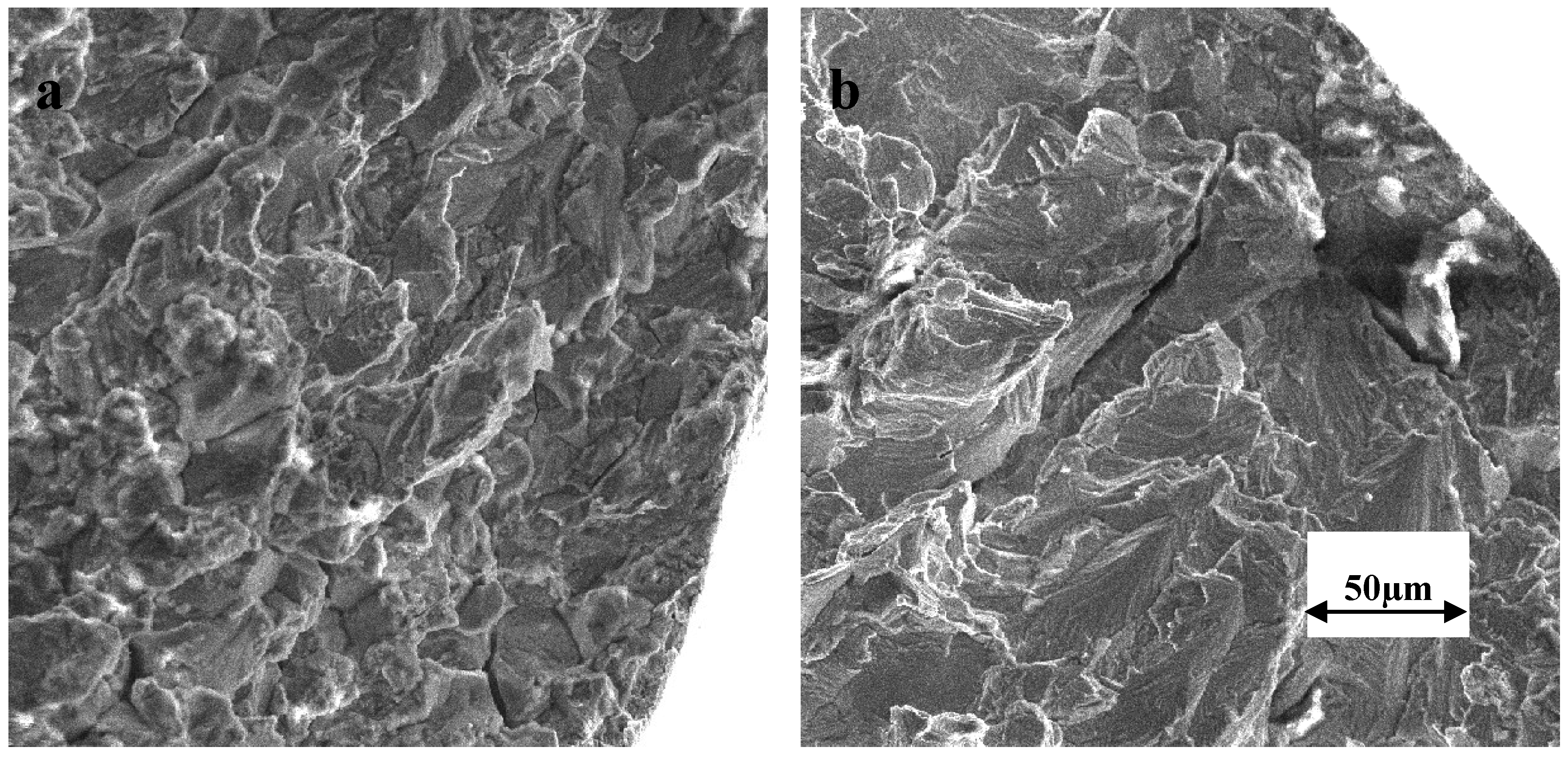
If the atmosphere contains halides this can leave any stainless steel susceptible to chloride stress corrosion cracking ciscc.
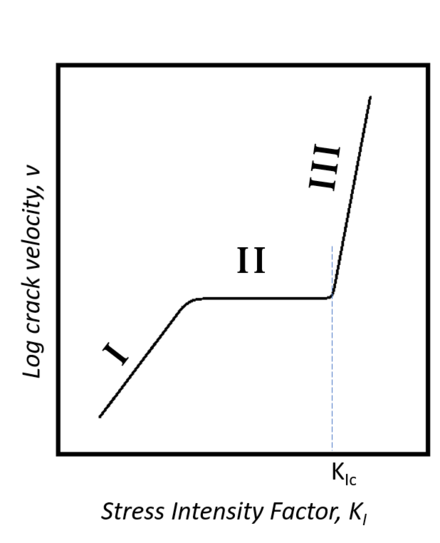
Chloride stress corrosion cracking stainless steel temperature. This mode of attack is termed stress corrosion cracking scc. Chloride stress corrosion cracking cscc is a type of intergranular corrosion. The hsl research report 902 reference 1 covers the susceptibility of stainless steel to ciscc in some detail and links to other research papers and published documents. A precursor of stress corrosion cracking in chloride bearing environments is pitting corrosion occurring if the stainless steel is not sufficiently resistant to pitting.
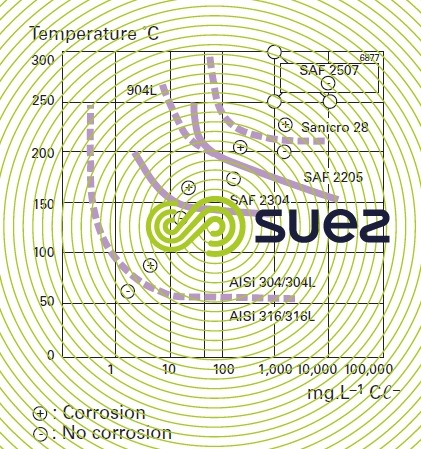
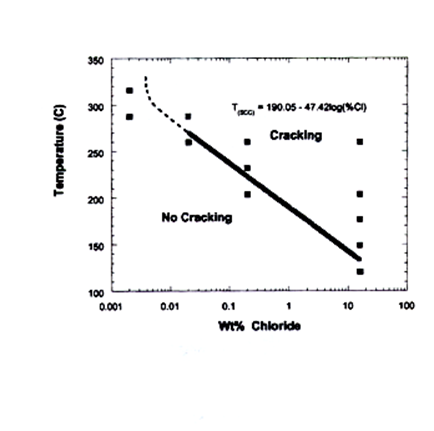
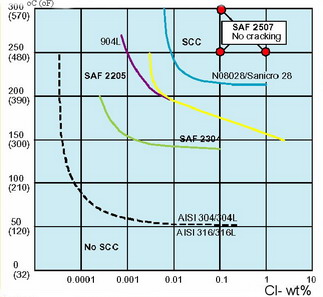
The temperature thresholds are well above the 212 f 100 c range indicating that exposures to atmospheric boiling in neutral chloride solutions are very unlikely to produce cracking. Chloride stress corrosion cracking definition. Although no stainless steel grade is totally immune. The most common environmental exposure condition responsible for scc of stainless steels is the presence of chlorides.
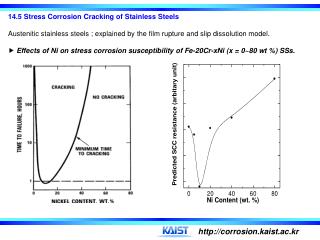
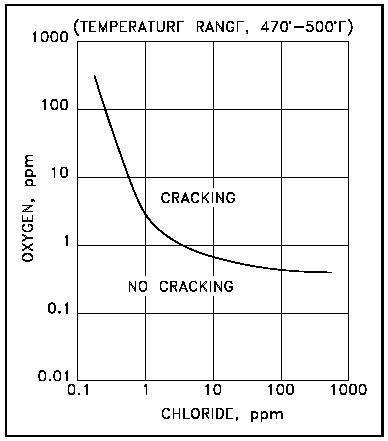
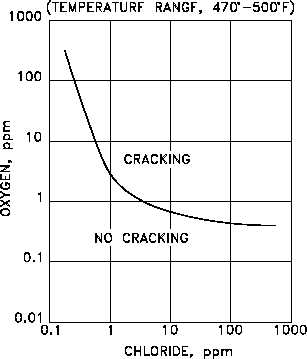
The cracking threshold of a 6mo super austenitic stainless steel uns n08367 immersed in oxygen bearing neutral chloride solutions is shown in figure 3. It can be detrimental to austenitic stainless steels one of the main reasons these steels are not considered a cure all for corrosion problems. Chloride stress corrosion is a type of intergranular corrosion and occurs in austenitic stainless steel under tensile stress in the presence of oxygen chloride ions and high temperature. Stress corrosion cracking scc is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment.
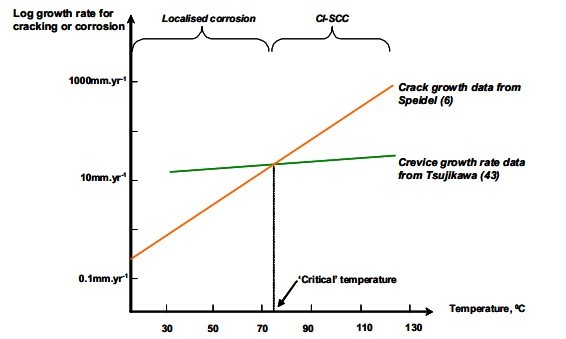
Deterioration by clscc can lead to failures that have the potential to release stored energy and or hazardous substances. It occurs in austenitic stainless steel under tensile stress in the presence of oxygen chloride ions and high temperature. Chloride stress corrosion cracking clscc is one the most common reasons why austenitic stainless steel pipework and vessels deteriorate in the chemical processing and petrochemical industries. The combination of tensile stress and a specific corrosive environment can crack stainless steels.
It is thought to start with chromium carbide deposits along grain boundaries that leave the metal open to corrosion. How to reduce the risk of stress corrosion cracking scc the risk of stress corrosion cracking scc can be minimized through plant and equipment design.



.gif)